Ice Safety
Here are some general guidelines on the strength of ice at different thicknesses.
- Just after freeze up, ice in the middle of the lake is thinner than ice along the shoreline.
- Check ice thickness by drilling test holes over the entire area that maybe used.
- Clear lake ice is the strongest.
- New ice is stronger than old ice, and ice formed by freezing slush and overflow is weaker than clear ice.
- Snow cover drastically slows freezing of ice by insulating it from cold air temperatures.
- Continuous travel over the same path will weaken thin ice.
- Keep weights spread out when working on thin ice.
- Cracking, currents and other inconsistencies will reduce the above load figures by up to a half.
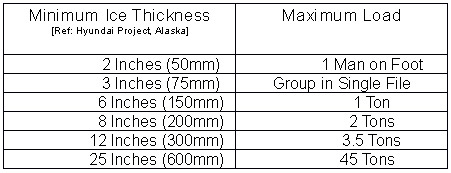
Ice Thickness and Strengths for various Loads
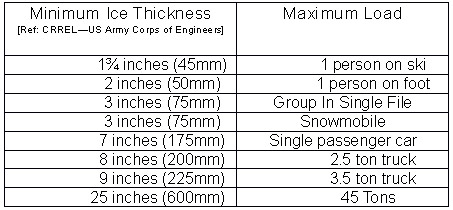
The load bearing capacity of ice covers depends on the quality of ice, its thickness, ice and air temperatures, temperature changes and solar radiation. Clear blue ice is the standard of quality against which other types of ice are compared. White opaque ice, or snow ice, is normally considered to be only half as strong.
Ice covers may consist of alternate layers of clear ice and snow ice, and each layer should be measured so that the effective thickness may be calculated. For example, an ice cover with a total thickness of 8 inches (20 cm) consisting of a 4 inch (10 cm) layer of clear ice and a 4 inch (10 cm) layer of snow ice would have an effective thickness of 6 inches (15 cm).
The strength of ice is generally increased by low temperatures. The increase is progressive from zero to minus eighteen degrees Celsius and remains fairly constant below this point. However, a marked drop in temperature can temporarily cause internal stress in an ice cover and reduce its bearing capacity. This can often occur during overnight periods when the temperature is much lower than the preceding average for the day.
The removal of snow from an ice cover during periods of low temperature has an effect similar to a marked temperature drop. The bearing capacity of ice should be considered to be reduced by 50 per cent for 24 hours after these conditions.
Leave a Reply
Recent Posts
Fume Cabinet Performance
30/04/2012 • The only statutory control relevant to the use of fume cabinets is the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations.... more
Ice Safety
30/04/2012 • Here are some general guidelines on the strength of ice at different thicknesses. Just after freeze up, ice in the middle... more
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
09/09/2011 • Paul Ramsden, Integral HSE’s principle consultant while be presenting a poster on the causes of carbon monoxide poisoning in Antactic... more





